Electricity, Magnetism, AC/DC Circuits
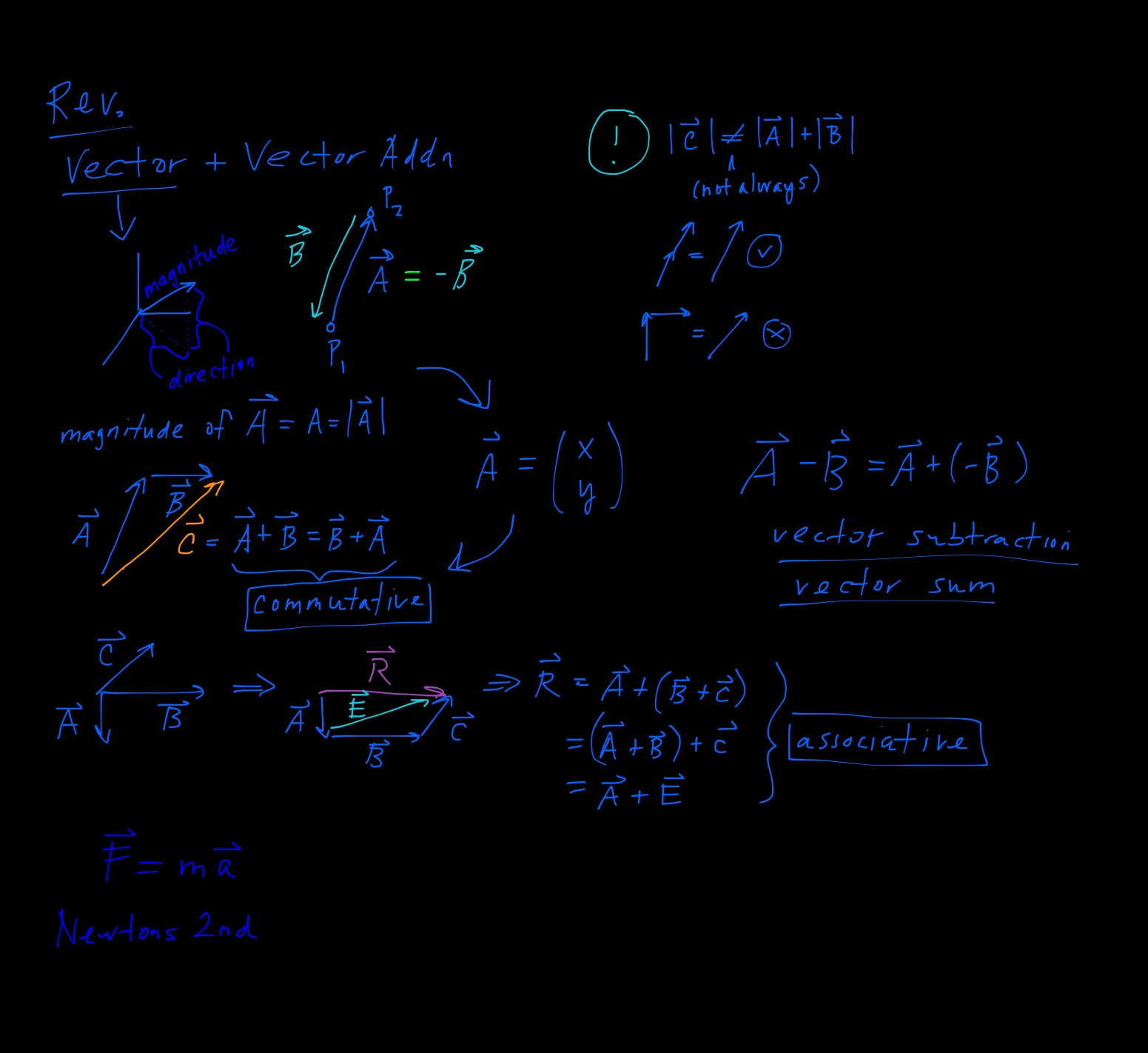
Review
Vectors & Vector Addition
Charge Density
$\rho = m/V = kg/m^3$
$\sigma = m/A = kg/m^2$
$\lambda = m/L = kg/m$
we can modify the equations so that mass ($m$) is Coulombs ($C$)
UNIT 1
You should know:
- Memorize the meanings of the common metric prefixes (p, n, µ, m, c, k, M) -The steps outlined in the problem solving guide.
- The meanings of key terms.
- The electron/proton model of electric charge, and how it explains the behavior of electric charges qualitatively.
- How to use Coulomb’s Law to calculate electric forces and field between point charges, including groups of many point charges.
- How to find the electric force or field created by a continuous charge distribution using integration.
- The meaning of the electric field.
- The meaning of the electric dipole moment and how it can be used to calculate fields, torques, and potential energies.
- How to calculate electric flux through a surface.
- How to use Gauss’ Law to determine the electric field in situations with strong symmetry.
- The arrangement of charges and fields on/near conductors.
UNIT 2
You should know:
- Memorize the meanings of the common metric prefixes (p, n, μ, m, c, k, M)
- p,
- n,
- μ,
- m,
- c,
- k,
- M,
- The steps outlined in the problem solving guides.
- The meanings of key terms.
- What a capacitor is and the definition of capacitance.
- capacitor
- capacitance
- The properties of a parallel plate capacitor, including the relationships between the dimensions of the capacitor, capacitance, potential difference, and electric field.
-
How capacitors behave in series and parallel.
- The energy stored in a capacitor/electric field.
- How dielectrics work and how they affect capacitance.
- The definitions of current density and current.
- The definitions and relations between resistance and resistivity, and how these quantities are related to Ohm’s Law.
- How to draw and interpret circuit diagrams.
- How energy and power are transferred in electric circuits.
- How resistors behave in series and parallel.
- How to analyze DC circuit behavior conceptually.
- How to use Kirchoff’s laws to analyze circuits.
- The rules, concepts, and mathematics governing RC circuits (charging and discharging).
While the target of the test is chapter 23-26 material, since the material is cumulative, you should also know the following material from previous sections:
- The electron/proton model of electric charge, and how it explains the behavior of electric charges qualitatively.
- How to use Coulomb’s Law to calculate electric forces and field between point charges, including groups of many point charges.
-
How to find the electric force or field created by a continuous charge distribution using integration.
- The meaning of the electric field
- represented by electric field lines, which is a representation of forces applied by the interaction of charges